
Neodymium Magnets
Our mission is to manufacture high-quality NdFeB permanent magnets in close co-operation with the customers in order to find the most suitable and cost effective solution.
Build Your Custom MagnetShape and specification
Nd-Fe-B magnet are mostly non-standard parts. The shape and size of magnet are generally processed according to customers’ requirements, such as segment, square, cylinder, ring and other special shape, The largest size of large-size products can reach to 200mm×200mm×80mm.
 Arc type |
 Disc type |
 Ring type |
 Rod type |
 Block type |
 Sphere type |

Rare Earth Cylindrical Magnets N35 D5x3
Neodymium Disc Magnets,D5x3, Ni-Cu-Ni, Grade_N35

Neodymium Rare Earth Disc Magnets N35 D4x5
Neodymium Disc Magnets,D4x5, Ni-Cu-Ni, Grade_N35

Round Magnet Neodymium N35 D4x2
Neodymium Disc Magnets,D4x2, Ni-Cu-Ni, Grade_N35
The surface treatment
Neodymium magnets are prone to corrosion in humid environments. For protective measure for corrosion resistance, Magnetic Hold offers nickel, zinc, tin, silver, gold plating and spray coating epoxy resin.
| Pctures |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Coating | Zinc | Nickel | Gold | Silver | Epoxy | Parylene |
| Thickness | 7-15um | 15-21um | 16-23um | 16-23um | 20-38um | 10-15um |
| Salt spray test | 12 hours | 24 hours | 36 hours | 24 hours | 48 hours | 48 hours |
Magnetization
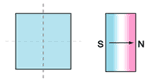 oriented through thickness | 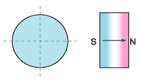 axially oriented | 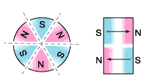 axially oriented in segments |
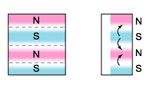 oriented laterally | 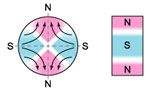 multipole oriented in segments on outside diameter* | 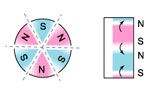 multipole oriented in segments on one face |
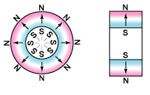 radially oriented * | 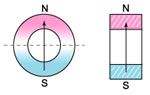 oriented through | 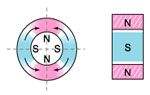 multipole oriented in segments on inside diameter* |
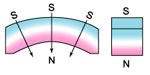 radially oriented | 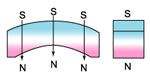 diametrically oriented | all available as isotropic or anisotropic material * only available in isotropic and certain anisotropic materials only |
Application
NdFeB magnet is widely used in Machinery, Video and Audio equipments, Communication Devices, Medical Devices, Office Automation Equipments, Space Flight and Aviation, etc. Our magnets are mainly used for motors and generators, such as Elevator Motors. Wind Turbines, Servo Motors, Motors for Hybrid Electric Vehicle, Battery Electric Vehicles, Linear motors and Compressor Motors etc.

Block Magnet for Automobile |

Permanent Arc Magnet for Servo Motor |

Nd Magnet for Wind Turbine |

Nd Magnet for Elevator Motor |

Magnets For High- speed Motors |

Magnets for Wind Turbine Generators |
Neodymiu Magnet Grade
Many grades of Neodymium magnets exist to support a variety of industrial applications. The range of Neo grades typically extends from 33 MGOe to 52 MGOe. This range allows for optimizing cost, performance, and operational temperature resistance.
The typical convention for “Grade” is to use the value of the particular magnet alloy’s Energy Density or Maximum Energy Product. Oftentimes there are letters or a two digit number suffix attached to the Grade which indicates the Intrinsic Coercive Force (Hci) level of the magnet alloy. This Hci is a good indicator of the maximum allowable temperature a particular Neo alloy can tolerate before irreversible demagnetizing occurs.
The higher the “Grade number” then the higher the Energy Density. Usually the higher the Energy Density the stronger the magnet, but this is very much dependent upon the magnet’s operational environment.
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N35 | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N38 | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N40 | 12.6-12.9 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 38-40 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N42 | 13.0-13.2 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 40-42 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N45 | 13.3-13.7 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 43-45 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N48 | 13.8-14.2 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >12 KOe | 45-48 MGOe | 80C / 176F |
| N50 | 14.1-14.5 KGs | >11.0 KOe | >11 KOe | 48-50 MGOe | 60C / 140F |
| N52 | 14.5-14.8 KGs | >11.2 KOe | >11 KOe | 49.5-52 MGOe | 60C / 140F |
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N35M | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N38M | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N40M | 12.6-12.9 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 38-40 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N42M | 13.0-13.3 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 40-42 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N45M | 13.3-13.7 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 42-45 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N48M | 13.6-14.2 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 45-48 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| N50M | 14.1-14.5 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >14 KOe | 48-50 MGOe | 100C / 212F |
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N33H | 11.4-11.7 KGs | >10.3 KOe | >17 KOe | 31-33 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N35H | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >10.8 KOe | >17 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N38H | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >17 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N40H | 12.6-12.9 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >17 KOe | 38-40 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N42H | 13.0-13.3 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >17 KOe | 40-42 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N45H | 13.3-13.7 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >17 KOe | 42-45 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| N48H | 13.6-14.2 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >16 KOe | 45-48 MGOe | 120C / 248F |
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N30SH | 10.8-11.2 KGs | >10.1 KOe | >20 KOe | 28-30 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N33SH | 11.4-11.7 KGs | >10.3 KOe | >20 KOe | 31-33 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N35SH | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >10.8 KOe | >20 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N38SH | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >20 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N40SH | 12.6-12.9 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >20 KOe | 38-40 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N42SH | 13.0-13.3 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >20 KOe | 40-42 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| N45SH | 13.3-13.7 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >19 KOe | 43-45 MGOe | 150C / 302F |
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N28UH | 10.4-10.8 KGs | >9.8 KOe | >25 KOe | 26-28 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| N30UH | 10.8-11.2 KGs | >10.1 KOe | >25 KOe | 28-30 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| N33UH | 11.4-11.7 KGs | >10.3 KOe | >25 KOe | 31-33 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| N35UH | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >10.8 KOe | >25 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| N38UH | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >25 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| N40UH | 12.6-12.9 KGs | >11.4 KOe | >25 KOe | 38-40 MGOe | 180C / 356F |
| Grade | (BR) | (HCb) | (Hcj) | (BH)max | Tmax |
| N30EH | 10.8-11.2 KGs | >10.1 KOe | >30 KOe | 28-30 MGOe | 200C / 392F |
| N33EH | 11.4-11.7 KGs | >10.3 KOe | >30 KOe | 31-33 MGOe | 200C / 392F |
| N35EH | 11.7-12.1 KGs | >10.8 KOe | >30 KOe | 33-35 MGOe | 200C / 392F |
| N38EH | 12.2-12.6 KGs | >10.8 KOe | >30 KOe | 36-38 MGOe | 200C / 392F |
Did You Know?
The factors can affect a magnet’s strength:
- Heat
- Radiation
- Strong electrical currents in close proximity to the magnet
- Other magnets in close proximity to the magnet
(Neo magnets will corrode in high humidity environments unless they have a protective coating.)
Shock and vibration do not affect modern magnet materials, unless sufficient to physically damage the material.